How to Choose the Right Position Sensor for Your Needs?
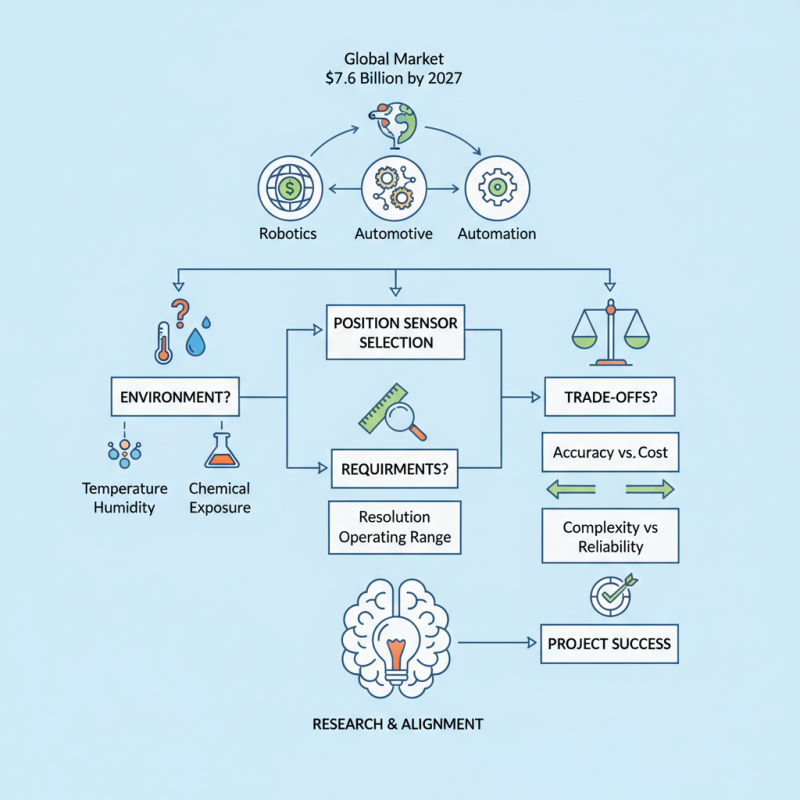
Selecting the right Position Sensor can significantly impact your project’s success. The global market for position sensors is projected to reach $7.6 billion by 2027. This growth is driven by industries like robotics, automotive, and automation, which rely heavily on these devices.
Position sensors play a critical role in ensuring precision in various applications, from manufacturing to aerospace. They convert the physical position of an object into an electrical signal. However, choosing the wrong type can lead to inaccuracies and inefficiencies, which can be costly.
Understanding the specific requirements of your application is essential. Consider the environment where the sensor will operate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals cannot be overlooked. It's also vital to assess the sensor's resolution and operating range. Many designs may seem appealing, yet they might not meet all your demands. Recognizing the trade-offs is key. Investing time in research will ensure that your Position Sensor choice aligns with your project goals.
Understanding Position Sensors: Types and Applications
Position sensors play a crucial role in various applications across industries. They convert the position of an object into an electrical signal. Common types include potentiometers, capacitive sensors, and inductive sensors. According to industry reports, the global position sensor market was valued at approximately $3 billion in 2020, with an expected growth rate of around 7% annually over the next few years.
Understanding different types of position sensors helps in choosing the right one. For example, potentiometers are often used in robotics for precise control. Capacitive sensors are favored in touch applications. Meanwhile, inductive sensors excel in harsh environments. However, the wrong choice can lead to inefficiencies. In some cases, the technology may not suit the application, resulting in inaccurate readings or even failure.
Moreover, factors such as operating range, environmental conditions, and budget are vital considerations. Each sensor type has its strengths and weaknesses. Unsuitable environments can diminish sensor performance. Ignoring these factors can lead to costly mistakes. Ensuring compatibility with your system is essential for optimal performance.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Position Sensor
When choosing the right position sensor, several key factors play a crucial role. Understanding the environment is essential. For example, an industrial setting may have dust or moisture that influences sensor selection. According to a recent industry report, 60% of position sensor failures stem from environmental factors. Thus, selecting a sensor with appropriate IP ratings is vital.
Accuracy and resolution are equally important. Different applications require varying levels of precision. For instance, robotics may demand a much higher resolution than basic automation processes. Research shows that 75% of engineers cite accuracy as a top consideration in their selections. Reflecting on this, one must assess how tightly requirements align with the sensor's capabilities. Any lack of clarity can lead to costly mistakes.
Additionally, the communication interface can complicate decisions. Modern sensors often integrate with various systems, using protocols like CAN or Ethernet. Ensuring compatibility can save future headaches. Yet, many projects overlook this, risking integration issues down the line. Therefore, it's crucial to reflect on system requirements and potential scalability as needs evolve.
Assessing Accuracy and Resolution Needs for Your Project
When choosing a position sensor, accuracy and resolution are critical. First, consider the specific needs of your project. If precision is paramount, invest time in understanding how resolution affects performance. A high-resolution sensor might provide minute detail, but does it match your actual requirements? Sometimes, lower resolution may suffice.
Think about the environment as well. Sensors often behave differently in various conditions. For instance, high humidity can impact readings. You might find that a sensor with less accuracy performs better in your setting. Testing different types can reveal unexpected insights.
Don't overlook the long-term implications. An overly sensitive sensor can lead to excessive data noise. It might complicate your analysis. Evaluate your project's goals carefully. Balancing accuracy and resolution with practicality is essential. Each choice should reflect not only current needs but also future demands.
Evaluating Environmental Conditions for Sensor Compatibility
When selecting a position sensor, understanding environmental conditions is key. Various elements, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals, influence sensor performance. For instance, high humidity can lead to inaccurate readings or failure. Assess where and how the sensor will be deployed.
Consider the temperature range of your application. Extreme temperatures can affect sensitivity and response times. Make sure the sensor is rated for your specific environment. For outdoor use, consider the effects of rain, dust, or UV exposure. Choose a housing that protects against these elements.
**Tip:** Always review the manufacturer’s specifications. Look for IP ratings, which indicate how well a sensor can withstand environmental factors.
Another important factor is vibration. High levels of vibration can affect sensor stability. If your application involves moving machinery, look for sensors designed to handle such conditions.
**Tip:** Think about maintenance. Some sensors may need regular checks in harsh environments. Plan accordingly to ensure long-term reliability.
How to Choose the Right Position Sensor for Your Needs?
| Sensor Type | Environmental Conditions | Operating Temperature (°C) | Humidity Resistance (%) | Vibration Resistance (g) | IP Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Sensor | Indoor/Outdoor | -40 to 85 | 10-90 | 20 | IP67 |
| Optical Sensor | Indoor | 0 to 50 | 0-100 | 10 | IP54 |
| Ultrasonic Sensor | Outdoor | -20 to 60 | 20-80 | 15 | IP65 |
| Capacitive Sensor | Indoor | -25 to 70 | 5-95 | 20 | IP54 |
Budgeting for Position Sensors: Costs and Long-term Value
When selecting position sensors, budgeting is a vital factor. According to a recent industry report, position sensors can range from $20 to over $1,500, depending on technology and precision. For smaller projects or prototypes, a cost-effective choice may suffice. However, spending more upfront can lead to significant long-term savings. High-quality sensors offer improved accuracy and longevity. They minimize the need for replacements.
Budgeting should also consider maintenance costs. Some sensors require regular calibration. This can add expenses. Reports show that neglected maintenance leads to a 30% increase in operational costs over time. Understanding the total cost of ownership is essential. An initial low-cost sensor might seem appealing, but the hidden costs could outweigh the benefits.
Reflecting on past projects, some companies regretted their choice of sensors. Their savings were short-lived due to frequent failures. Investing in durable, reliable sensors often pays off in efficiency. Making the right choice hinges on balancing initial costs and long-term value. Choosing wisely can protect your project from unforeseen expenses.
 English
English  Français
Français 